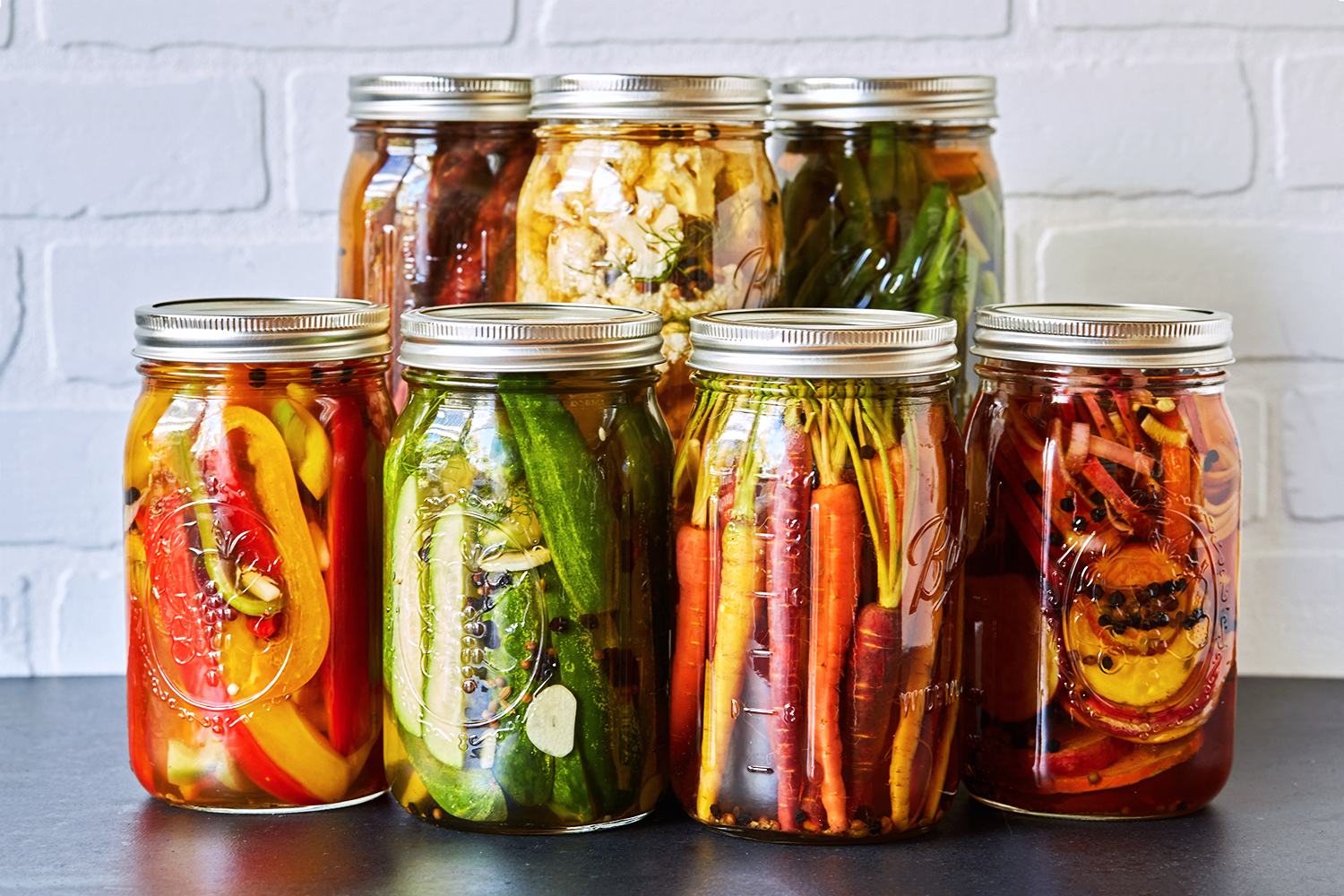
Mastering the Art of Vegetable Preservation: Unleash Your Inner Pickler
As the gardening season reaches its peak, many enthusiasts find themselves awash with fresh vegetables, eager to preserve the bounties of their labor. An ancient practice, pickling not only extends the life of your harvest but also transforms the flavors, offering a delightful addition to your culinary repertoire. In this article, we explore the ins and outs of vegetable pickling, ensuring your home preserves are both delicious and safe.
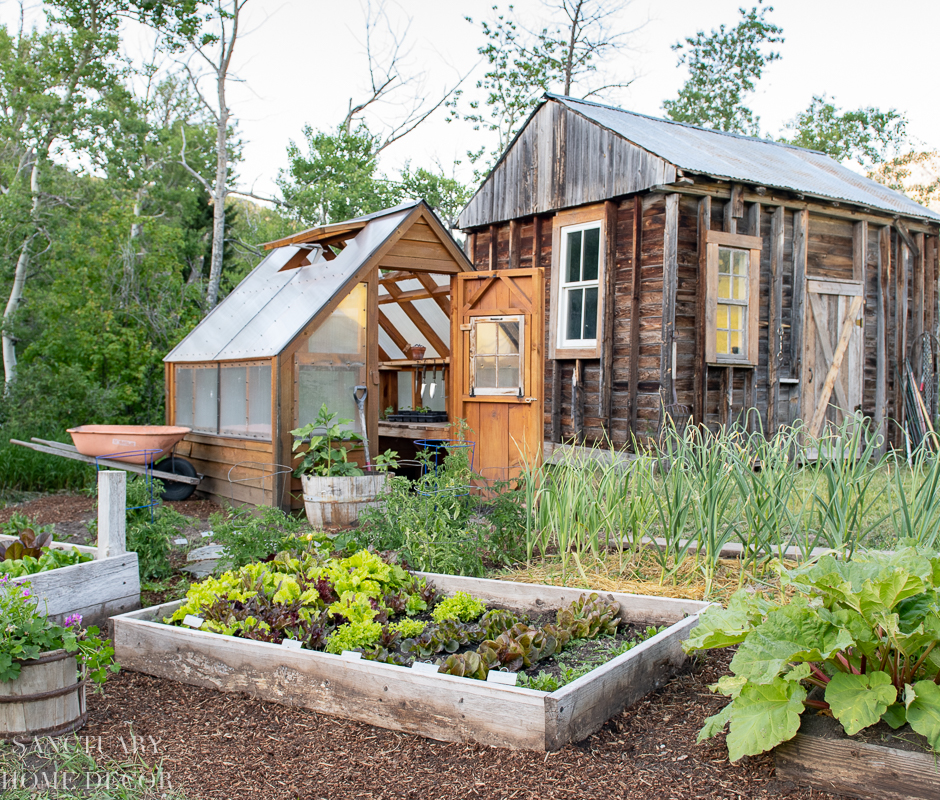 Exploring the treasures of your home garden
Exploring the treasures of your home garden
Understanding the Basics of Pickling
Pickling is essentially a method of food preservation that involves immersing vegetables in a brine solution or acid. Whether you opt for the classic vinegar-based method or the salt brine fermentation process, understanding the underlying principles is crucial.
Choosing the Right Vegetables
Some vegetables are particularly well-suited for pickling, while others may not yield the best results. Cucumbers, radishes, carrots, and green beans are popular choices. Their firm textures hold up well under the pickling process and absorb the brine flavors efficiently. Experimenting with different varieties can yield interesting flavors, but start with a few tried-and-true options to hone your techniques.
Preparing Vegetables for Pickling
Properly preparing your vegetables is essential for a successful pickling venture. Begin by thoroughly washing them to remove any dirt or pesticides. Depending on the type of vegetable and your personal preference, you might want to peel, slice, or leave them whole.
Maintaining Freshness
The freshness of your produce affects not just the taste but also the texture and safety of the final product. Always use the freshest vegetables and eat seasonal produce when available. Local farmers’ markets can be an excellent source of high-quality ingredients.
 The transformation of fresh veggies into tangy treats
The transformation of fresh veggies into tangy treats
Exploring Different Pickling Techniques
There are two main techniques for pickling: quick pickling and fermentation. Quick pickling (or refrigerator pickling) involves immersing the vegetables in vinegar and letting them sit for a short period, while fermentation relies on lactobacillus bacteria to form a brine and typically requires a longer time to develop flavors.
Quick Pickling
Quick pickling is a straightforward method, perfect for beginners. Simply prepare your vegetables, make a simple brine with vinegar, water, sugar, and salt, and pour it over the veggies in a jar. Allow them to sit in the fridge for at least 24 hours before tasting.
“Quick pickles are ready to eat in just a few hours, making them a convenient solution for impromptu gatherings.”
Fermentation
If you’re feeling adventurous, fermentation can produce profound, complex flavors that quick pickling simply cannot match. This process encourages the growth of beneficial bacteria. To ferment your vegetables, submerge them in a brine solution (usually a mix of salt and water) and allow them to sit at room temperature for several days to weeks. The unique flavors that develop during this time can be breathtaking.
Safety First: Guidelines for Successful Preserving
Pickling is generally safe, but it’s essential to follow some basic safety guidelines. Use clean jars and utensils to prevent the growth of unwanted bacteria. Make sure that your vegetables are fully submerged in the brine to reduce the risk of spoilage. If you’re new to pickling, consider following established recipes from reliable sources to ensure you’re using the right proportions and methods.
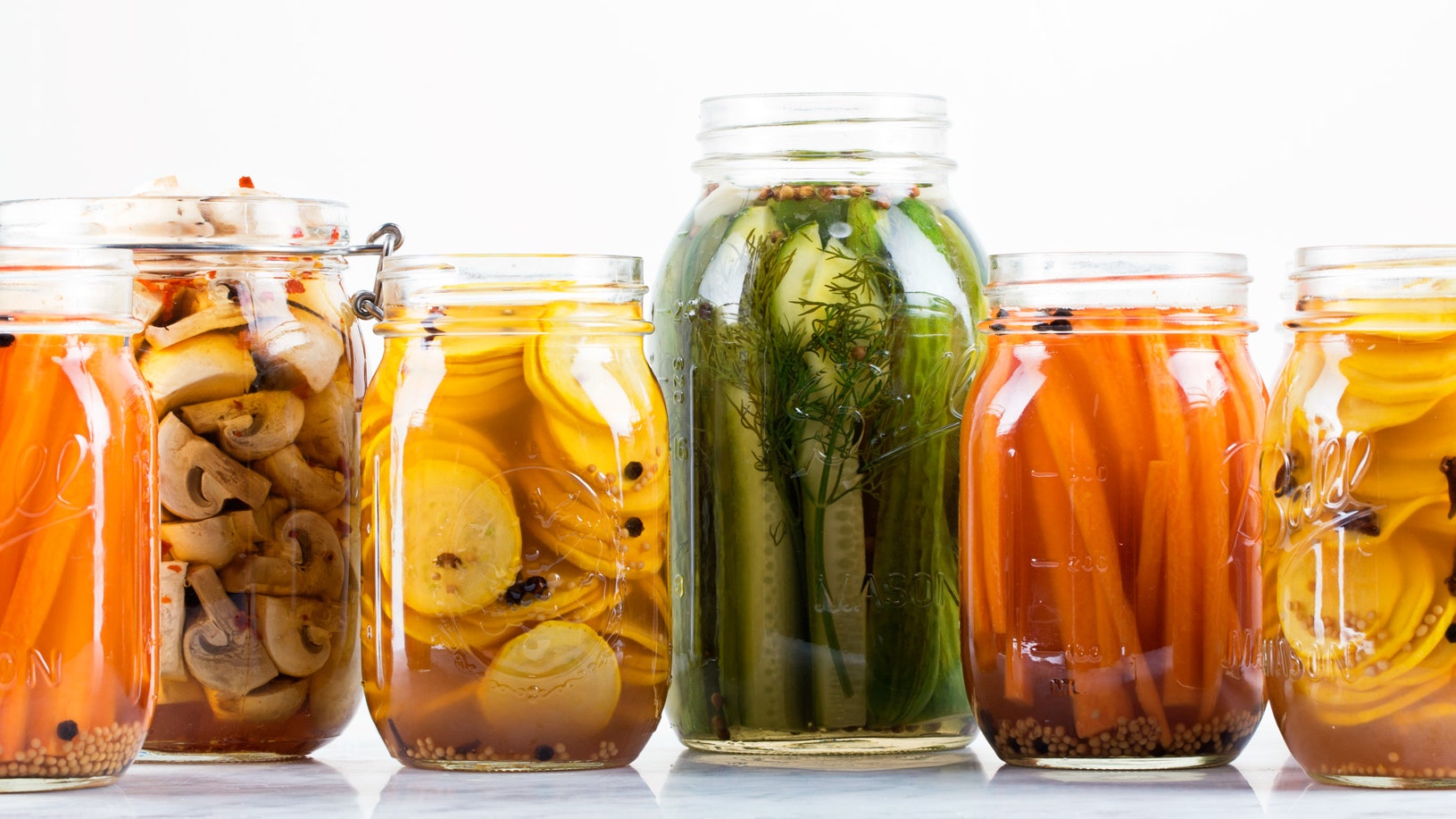 Colorful jars of pickled delights ready to be stored
Colorful jars of pickled delights ready to be stored
Storing Your Pickled Treasures
Once you’ve perfected your pickling process, proper storage will ensure your creations last. Most pickled vegetables can be stored in the refrigerator for several months, while fermented options can last even longer when kept in cool, dark places. Always check for signs of spoilage—such as mold, off-smells, or fizzing—before consuming.
Conclusion: Join the Pickling Movement
As the harvest season approaches its zenith, now is the perfect time to dive into pickling and discover the artistry and satisfaction of preserving your vegetables. Not only will you extend the life of your garden produce, but you’ll also intrigue your taste buds with rich, tangy flavors. So, grab your jars, gather those fresh veggies, and become part of the vibrant community of pickling enthusiasts!
Get ready to unleash your inner pickler and elevate your home canning game this season!